 https://www.synyo.com/wp-content/uploads/SYNYO-NEWS-featured-image-NEW01007705EN.png
400
459
leo
https://www.synyo.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/synyo-logo.png
leo2025-01-01 10:47:112025-02-10 10:48:51BOND: Outcomes in Advancing Education, Tolerance and Heritage Preservation to combat Antisemitism
https://www.synyo.com/wp-content/uploads/SYNYO-NEWS-featured-image-NEW01007705EN.png
400
459
leo
https://www.synyo.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/synyo-logo.png
leo2025-01-01 10:47:112025-02-10 10:48:51BOND: Outcomes in Advancing Education, Tolerance and Heritage Preservation to combat Antisemitism
SmartDataLake: A framework for making data lakes smart
Data lakes are raw data ecosystems, where large amounts of diverse data are retained and coexist. They facilitate self-service analytics for flexible, fast, ad hoc decision making. SmartDataLake enables extreme-scale analytics over sustainable big data lakes.
SmartDataLake provides an adaptive, scalable and elastic data lake management system that offers: (a) data virtualization for abstracting and optimizing access and queries over heterogeneous data, (b) data synopses for approximate query answering and analytics to enable interactive response times, and (c) automated placement of data in different storage tiers based on data characteristics and access patterns to reduce costs.
The data lake’s contents are modelled and organised as a heterogeneous information network, containing multiple types of entities and relations. Efficient and scalable algorithms are provided for: (a) similarity search and exploration for discovering relevant information, (b) entity resolution and ranking for identifying and selecting important and representative entities across sources, (c) link prediction and clustering for unveiling hidden associations and patterns among entities, and (d) change detection and incremental update of analysis results to enable faster analysis of new data.
Interactive and scalable visual analytics are provided to include and empower the data scientist in the knowledge extraction loop. This includes functionalities for: (a) visually exploring and tuning the space of features, models and parameters, and (b) enabling large-scale visualizations of spatial, temporal and network data. The results of the project are evaluated in real-world use cases from the business intelligence domain, including scenarios for portfolio recommendation, production planning and pricing, and investment decision making.
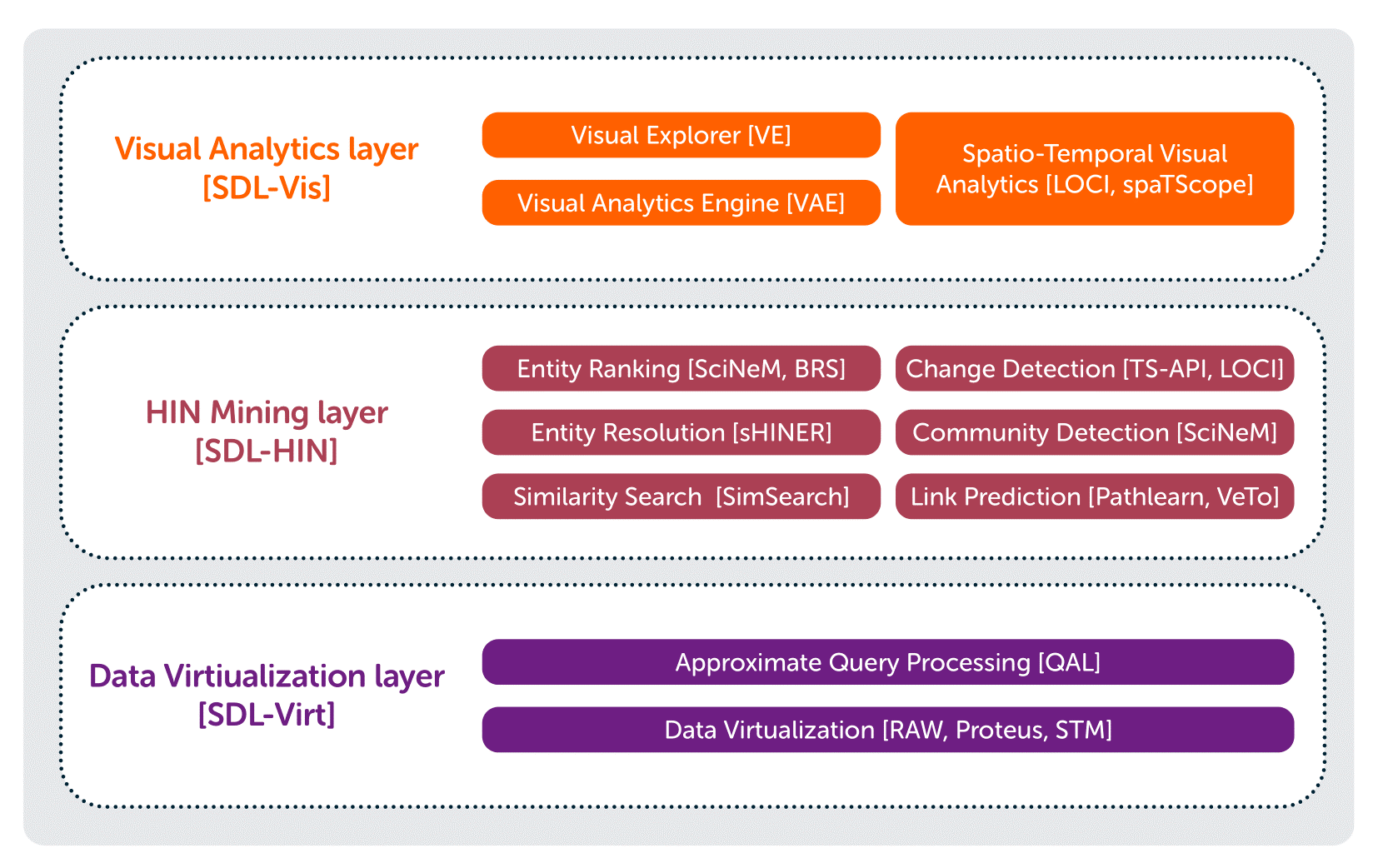
SDL-Virt
SDL-Virt: This layer is responsible for delivering efficient data access over a data lake containing large volumes of heterogeneous data. It encapsulates and abstracts all issues related to the efficient placement, distribution, management, and retrieval of data, providing upper layers homogeneous access to data through an SQL-like query language. Specifically, the main offered functionalities include: (i) data virtualization over different data types and formats, (ii) automated placement of data over different storage tiers to optimize the trade-off between storage cost and speed of retrieval, (iii) approximate query processing that can speed up data analysis by enabling approximate answers with theoretical guarantees for accuracy.
SDL-HIN
SDL-HIN: This layer is dedicated to searching and analysing the contents of a data lake, being represented in the form of a Heterogeneous Information Network (HIN), i.e., a graph consisting of entities and relations of different types. The offered functionalities include: (i) discovering similar or near-duplicate entities under different similarity criteria and matching conditions, (ii) ranking of entities based on the structure of the graph, as well as on other domain-specific criteria such as properties of geospatial regions, (iii) predicting or suggesting links between entities based on their attributes and position in the network, (iv) detecting communities of entities, including potentially overlapping or hierarchical communities, and (iv) detecting changes in evolving communities and in data represented as time series.
SDL-Vis
SDL-Vis: This layer includes the human in the data analysis loop through offering visual analytics capabilities building on top of the functionalities implemented in the two lower layers. Using a visual analytics model at its core to determine user interactions, it offers visualizations for supporting data profiling and parameter tuning. It also offers custom visualizations for specific types of data, including graph, spatial, and temporal. Further, individual components typically also include some sort of UI which enables the user to interact with the component directly. This is primarily to support the idea of keeping the component of being capable of both working in unity, but also individually, thus reducing the interdependencies between the components.
Links
https://smartdatalake.eu/
https://github.com/smartdatalake
Keywords
Big data, virtualization, data visualization, heterogenous graphs, meta-path, scalability




